Netlogic Consultancy and services LTD
Understanding Phishing Attacks: From Basics to AI Evolution and Detection Tips

Phishing attacks remain one of the most common cyber threats, tricking countless individuals and organisations into compromising their security. In this post, we’ll explore what phishing entails, how artificial intelligence has transformed these attacks, and practical ways to identify and avoid them. By staying informed, you can better protect yourself in an increasingly digital world.
What Are Phishing Attacks?
At its core, phishing is a deceptive tactic used by cybercriminals to lure people into sharing confidential details, such as login credentials, financial information, or personal data. Attackers often masquerade as reputable sources—like banks, government agencies, or familiar companies—to gain trust and prompt victims to click malicious links, download harmful files, or provide sensitive info directly.
These attacks typically occur through emails, but they can also manifest as text messages (smishing), phone calls (vishing), or even social media interactions. For instance, a classic email phishing attempt might claim there’s an issue with your account and urge you to “verify” it via a fake website that steals your details.
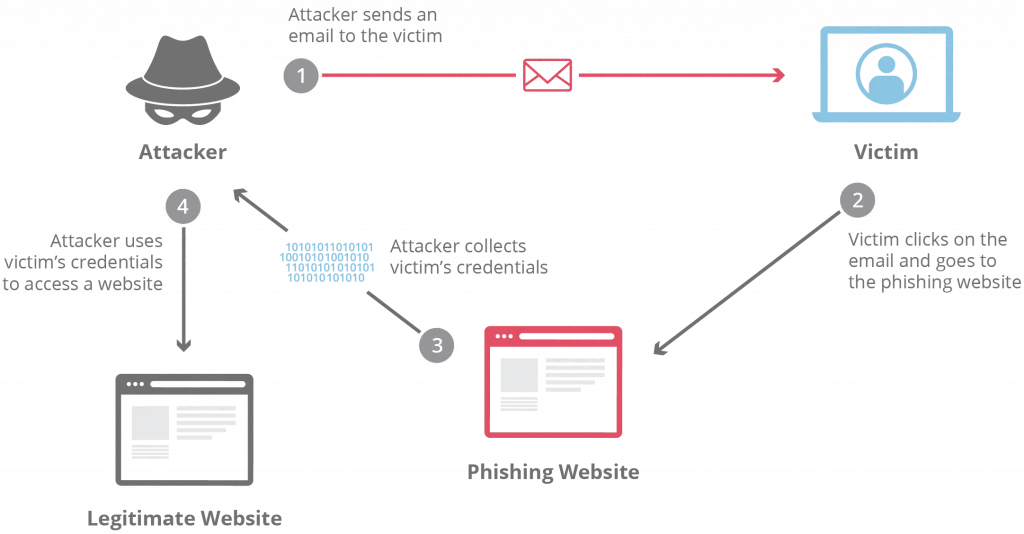
What is phishing? | Phishing attack prevention | Cloudflare
Over time, phishing has grown more sophisticated, moving from broad, scattershot campaigns to targeted strikes known as spear-phishing, where attackers research specific victims for higher success rates.
How Phishing Has Evolved with AI
Phishing isn’t new—it dates back to the 1990s—but the integration of AI has supercharged its effectiveness, making attacks faster, more personalized, and harder to detect. Traditionally, phishing relied on human effort to craft messages, often riddled with errors like poor grammar or obvious fakes. Now, AI tools enable attackers to automate and refine these efforts on a massive scale.
AI helps cybercriminals scrape public data from social media, company websites, and online profiles to create highly tailored messages that mimic real communications. For example, generative AI can produce thousands of customized emails in seconds, incorporating details like your recent job title or location to build credibility. This shift reduces the barrier for entry, allowing even novice hackers to launch convincing campaigns without deep technical skills. [hoxhunt.com]
Recent studies highlight the rapid growth: AI-assisted cyber threats rose by 72% from 2024 to 2025, with phishing incidents surging over 1,200% due to AI’s role in generating content. Another analysis shows that more than 73% of phishing emails in 2024 incorporated AI elements, escalating to over 90% for adaptive, polymorphic attacks that change to evade detection. In industries like finance, deepfake impersonations—where AI creates fake audio or video of executives—have increased by 15% in the past year. [totalassure.com , brside.com, hoxhunt.com]
AI also enables multi-channel strategies, combining emails with voice cloning or video deepfakes for seamless deceptions. Research from academic sources notes that while AI aids in detection tools, it’s equally weaponised by attackers to craft advanced threats, including polymorphic emails that evolve based on victim interactions. Projections indicate AI will dominate phishing by making it cheaper and more widespread, with trends showing quick adoption similar to past innovations like QR code scams. [mdpi.com, hoxhunt.com]
Real-World Examples of AI-Enhanced Phishing Attacks
To illustrate the dangers, consider the “Deepfake CEO Scam,” where attackers used AI-generated video calls to impersonate company leaders, pressuring employees into approving fraudulent wire transfers. In one documented case, a finance team member was tricked into sending millions after a realistic deepfake video mimicked the CEO’s voice and appearance. [sprocketsecurity.com]

Another example involves AI-powered social engineering on platforms like LinkedIn. Cybercriminals use AI to analyze profiles, generate personalized messages, and build fake connections that lead to data breaches or malware installation. Polymorphic email attacks, which AI adapts in real-time, have targeted organizations by morphing content to bypass filters—resulting in a 700% rise in credential theft incidents by late 2024. [sprocketsecurity.com, censinet.com]
In a notable 2025 incident, attackers employed AI voice scams to replicate executives in phone calls, with 30% of organizations reporting such events the previous year. These examples underscore how AI blurs the line between real and fake, amplifying the impact of phishing.
How to Spot and Avoid Phishing Scams
Detecting phishing requires vigilance, especially as AI eliminates telltale signs like spelling errors. Here are key indicators and strategies, drawn from expert guidance:
- Examine the Sender Carefully: Look for slight variations in email addresses, such as “” instead of the legitimate one. Always verify by checking the domain directly.
- Watch for Urgent or Threatening Language: Scams often create pressure with phrases like “immediate action required” or “your account will be suspended.” Pause and assess before responding.
- Inspect Links and Attachments: Hover over hyperlinks to reveal the true URL— if it doesn’t match the claimed site, it’s suspicious. Avoid downloading files from unknown sources.
- Generic Greetings or Unusual Requests: Messages starting with “Dear User” instead of your name, or asking for sensitive info like passwords, are red flags. Legitimate entities rarely request this via email.
- Independent Verification: If in doubt, contact the supposed sender through official channels, not the details provided in the message. For AI-enhanced threats like deepfakes, establish protocols like secret codes for high-stakes requests.
Additional tips include enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), using antivirus software with AI detection capabilities, and staying educated through regular training. Remember, if something feels off, break contact and report it to authorities like the FTC or your organization’s IT team.
Final Thoughts
Phishing attacks, empowered by AI, pose a growing risk, but awareness and caution can mitigate much of the danger. By understanding their mechanics, recognizing evolution through technology, and applying detection strategies, you empower yourself against these threats. Stay proactive, regularly update your knowledge and tools to outpace the scammers. If you’ve encountered a suspicious message, share your experience in the comments to help others!
- Tags:
- Cybercrime

